PERSONAL FINANCE FOR NOVICES-INSURANCE
There is always a risk of monetary loss in every human endeavour. The loss becomes easier to bear when it is shared within a community. For example, if a person loses his possessions worth $100,000, the paramount burden on that person, in this case, is reduced if ten people share the loss worth $10,000 each since every person
There is always a risk of monetary loss in every human endeavour. The loss becomes easier to bear when it is shared within a community. For example, if a person loses his possessions worth $100,000, the paramount burden on that person, in this case, is reduced if ten people share the loss worth $10,000 each since every person is more likely to possess $10,000 than $100,000. Similarly, 20,30 or maybe as many as 50 to 100 people sharing the loss can significantly reduce the burden on that person since it would be a minimal amount of loss bore by a larger group of the populace. This process of making loss more bearable is known as insurance. The process of managing the risk this way is time immaterial. Code of Hammurabi details how a merchant would pay some extra amount to a money lender so that he could get a debt waiver in case his goods are destroyed by a storm or looted by pirates. Millenniums later, today, we have complex working mechanisms of different types of insurance which we will analyze.
PROCESS BEHIND INSURANCE POLICIES
People generally approach an insurance broker whenever they want to insure something. An insurance broker is an expert in risk management. The insurance broker and his team interview the person to assess the risk and benefits of insuring him. For example, if a person is willing to get health insurance, the broker would assess the health of the person by reviewing the medical certificate, verifying whether the person smokes, drinks take drugs, or indulges in any other dangerous activity, verifying the past criminal record of the person if any. If the result of this analysis is unsatisfactory, the person can be denied insurance. Otherwise, the broker lists all the risks and benefits and presents them to an underwriter. Underwriting is a service provided by financial institutions through which a person who has incurred damage is awarded a monetary sum.

In contrast, the insurer or insurance company is the source of money. An insurance company may have one underwriter or a group of underwriters with a chief underwriter. The broker is obliged to strike a good deal with the underwriter in terms of coverage of the damage. The underwriter, meanwhile, reviews the list and may make changes if required. When a good deal is struck, the underwriter signs at the bottom of the paper describing risks and guidelines. The insured person is then required to pay the amount known as a premium to the insurance company. Premium amount is variable and is influenced by several factors. For example, in the case of health insurance, age and past medical history affect the premium amount. Broker is given 10% of the amount of premium as commission. In case of any damage, the broker must lay the claim for the best coverage. The money received from the underwriter is given to the insured without any deductions. In case there is no broker in this entire process, the person himself is required to negotiate deals, but it is a bit difficult since negotiation involves expertise. The insurance company is not always at a loss due to this as said insurance company works by collecting the funds from a large section of the populace which also pays the premium as required by the insurance policy. So they always hold a pool of money. Secondly, there is a reinsurance process through which the company can get insured for the losses from another company at a lower premium.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF INSURANCE POLICIES
Insurance policies are divided into two broad categories – life and general. General insurance is purchased for personal belongings like motor vehicles, homes or endeavours like travel and businesses. In contrast, life insurance is generally purchased by the bread earner of the family to ensure that her family survives in case she dies.
GENERAL INSURANCE
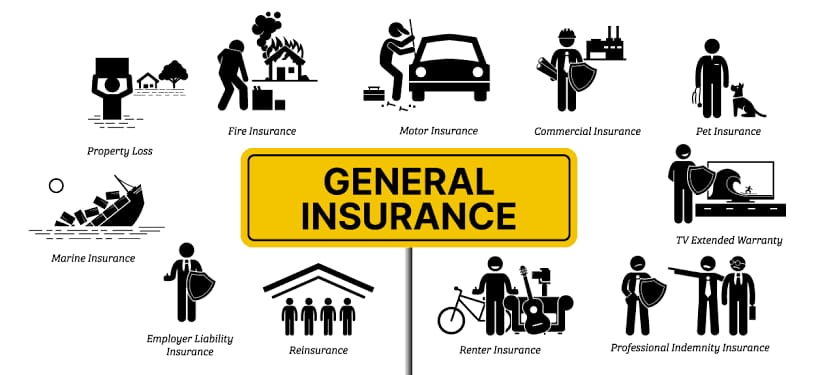
Broadly speaking, every insurance policy outside the domain of life insurance is general insurance. There are many types of general insurance, the most common of which are: 1. Health Insurance: Covers up the healthcare costs incurred by the insured. Every year, the insured must pay a certain amount of money for the healthcare he procures. This amount is called a deductible. That means the insurance company pays for the healthcare only when the deductibles are cleared. Plans with higher deductibles have a lower premium than plans with lower deductibles. There is also coinsurance, a percentage of healthcare cost to be paid by the insured herself or copay, a fixed sum (not the percentage) that must be paid by the insured every time she obtains a healthcare service. 2. Travel insurance: Covers up the damage of any form incurred during long-distance travel. 3. Commercial insurance: covers business-related losses like damage to the capital, goods, etc. Other types of insurance like home insurance, property insurance, marine insurance and motor insurance insure houses, properties, motor vehicles and ships, respectively.
LIFE INSURANCE

A life insurance policy sustains the insured's family once he has expired. There are broadly 5 types of life insurance policies: 1. Term Insurance: Under this policy, the person must pay the premium until the policy matures. In case of the person's demise within the term period, the family is given coverage for the remaining term time as detailed by the policy. In case the policy holder survives the maturity of the policy, i.e. end of the term period, he is not given any refurbishment or other rewards. This policy is most sought after because it has a low premium and high coverage. 2. Endowment plans: Under this plan, the person gets a life cover and resources to save regularly for a fixed period. When the policy matures, these savings are given back to the insured or the nominee as a lump sum amount and also gets maturity benefits with a bonus. Though it seems appealing, the premium for this plan is far higher than that for term insurance, and the coverage given is not as high as term insurance. 3. Unit Linked Insurance Plans (ULIPs): Under this plan, there is an insurance cover and an investment plan. As a result, these cannot guarantee returns. In this plan, the premium amount covers both insurance coverage and investment plans. Since the investment component is under insurance, the profits are entitled to tax benefits. Premium is very high in this case. 4. Money-Back Plans: Under this plan, the person is given a certain amount of his premium back. If the policy holder survives the maturity of his policy, maturity benefits are applicable. This policy is helpful for risk-averse individuals who wish to save throughout the insurance plan. However appealing the options other than Term Insurance may seem, term insurance has the upper hand in terms of coverage which is the primary purpose of an insurance policy. It is the opinion of experts that the coverage amount should always be at least 10 times the annual income of the person.
CONCLUSION
Insurance is a service that can give a person some certainty about the future. Current insurance policies are far cheaper than in the past due to cut-neck competition between companies. The global insurance market size is approaching $6T. Unfortunately, there is no shortage of frauds in the insurance industry. Moreover, most people don't read more about insurance policies before deciding to buy one. The consequence is that people remorse buying the policy once it ceases to entertain them up to their expectations. On the end note, we only advise the readers to increase their financial literacy regarding insurance which would come in handy when they wish to buy a policy in the future.
